This page is an introduction to the main components of the X-Max4 3D printer, which provides you with a general understanding of the printer.
¶ How does X-Max4 work?
X-Max4 3D printer is a machine that uses plastic wires to create 3D objects.
In most cases, X-Max4 can print 3D models in STL format, and slicing software is required to preprocess the file model before printing.
Taking QIDI Studio as an example, the slicing software will divide the STL file into many layers, and the information of each layer will be automatically converted into a language that the printer can understand, used to indicate the movement path and speed of each axis during the printing process.
In addition, slicing software can also integrate various parameter settings in the generated code, such as the printing temperature of the wire, the extrusion speed of the printer, and generate support for certain parts of the printing model.
¶ CoreXY motion system
The QIDI X-Max4 uses a CoreXY motion system controlled by two stepper motors. The X and Y stepper motors work together to move the printhead. New 1.5GT custom belt with higher tooth density for smoother, more precise motion. Minimizes vibration frequency artifact (VFA) for better print quality

Every stepper motor has an independent belt that is connected to the print head, so a pair of belts is used to control its position. Having a CoreXY motion system allows the X-Plus4 to print much faster compared to a traditional cartesian printer because the weight is lower, which is important when it comes to printing fast.
More information about the CoreXY motion system is available in this link.
¶ Z-axis
Dual independent Z motors with 2 mm lead screws, anti-backlash nuts, and the shortest Z travel in its class for unmatched precision and perfect layer alignment.
¶ extruder

The extruder is responsible for pulling the wire out of the spool and feeding it into the hot end. After heating and melting, it is extruded through a nozzle to generate a printed model. The extruder requires precise control of the length of the wire extruded through the hot end and is one of the core components of 3D printers.
¶ hotend
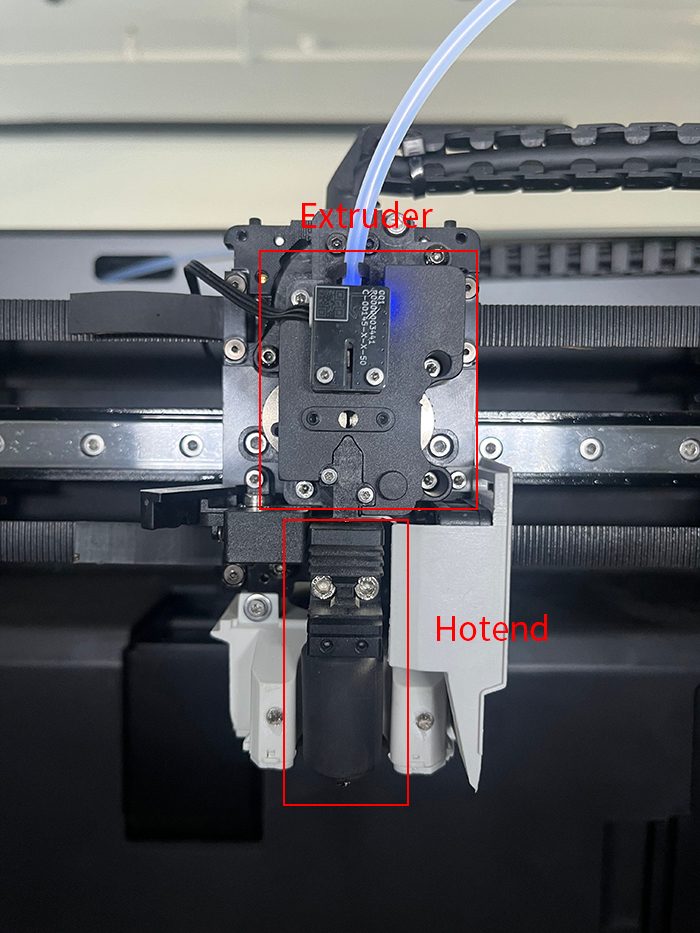
The hot end is responsible for heating the wire to a specified temperature, melting it, and depositing it in a thin layer to create a model. Different materials use different heating temperatures. For example, PLA wire needs to be printed at lower temperatures around 210-220 ° C, while other materials such as PETG and ABS require printing at higher temperatures around 250-260 ° C.
¶ Hotbed

A hot bed is used to heat the printing surface and help the printing layer adhere better to the frame plate.
When using the X-Max4 3D printer, the heating temperature is controlled according to the type of wire, and the maximum temperature can reach 110 ° C. For example, PLA material is printed on low-temperature printing panels using a hot bed temperature of 35-45 ° C without warping. To prevent warping, materials such as ABS and PC require a hot bed temperature of 100-110 ° C for printing.
If the printing surface is not heated, the deposited wire will quickly cool down, and the tension between layers will cause it to warp.