¶ X-Plus 4
¶ Front View
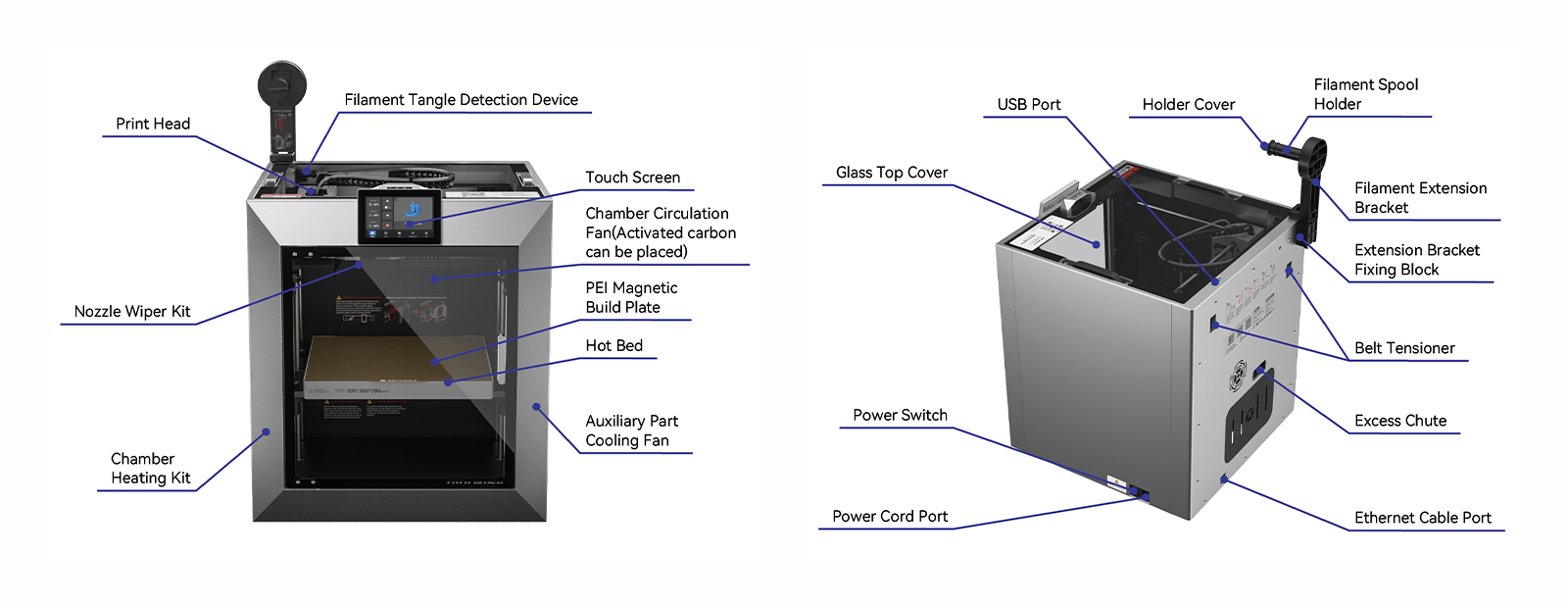
| Print Head | This component contains multiple parts, such as extruders, hot ends, tool head plates, etc. |
| Nozzle Wiper Kit | This component is used for cleaning nozzles. |
| Chamber Heating Kit | This component is used to increase the chamber temperature during sealed printing. |
| Filament Tangle Detection Device | Used to detect whether consumables are entangled. |
| Touch Screen | Display printing parameters and control the printer. |
| Chamber Circulation | The fan in the back of the printer which pulls air from inside the chamber, in order to regulate the inside air and ensure it does not over a specific temperature. |
| PEI Magnetic Build Plate | It is made by coating a stainless steel sheet with a layer of PEI powder, creating a textured surface on both sides. What sets it apart is its special rough texture, which is transferred to the bottom surface of your prints. This plate works well with a variety of materials and often provides excellent adhesion without the need for adhesives, making it user-friendly. Additionally, the PEI coating on the plates is durable and has a long lifespan. |
| Hot Bed | The main function of the heatbed is to heat the printing surface to help the printed layer adhere better to the build plate. If the printing surface is not heated, the first layer of filament deposited on the heatbed may not be able to stably adhere to the heatbed surface, causing the print to warp or even fall during subsequent printing. |
| Auxiliary Part Cooling fan | The large radial fan located on the right side panel, which is used for extra strong cooling. |
| Glass Top Cover | Used for sealing chambers for box printing. |
| Power Switch | Printer power switch. |
| Power Cord Port | Used for connecting power cords. |
| USB Port | Used for connecting USB interface storage. |
| Holder Cover | Used to fix the filament shaft. |
| Filament Spool Holder | Used for placing filament shafts. |
| Filament Extension Bracket | Used to place filaments above the printer. |
| Extension Bracket Fixing Block | Used to fix the filament extension bracket to the printer backplane. |
| Belt Tensioner | Used for tensioning XY belts. |
| Excess Chute | The waste generated during material and material replacement of the printer is discharged from the outlet. |
| Ethernet Cable Port | sed for connecting network cables. |
¶ Toolhead View
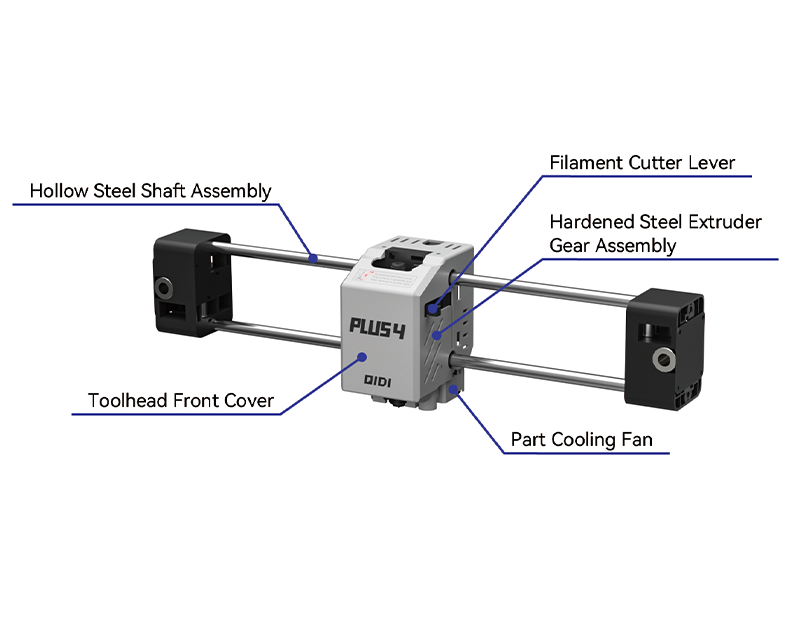
| Hollow optical axis component | Used to grip the cutting blade and push its cutting filaments. |
| Tool head front cover | The internal gear assembly of the extruder device consists of a transmission wheel and two extrusion wheels, which work together to feed the filament into the hot end. |
| Knife handle | To protect the front of the printer tool head, the tool head front cover of X-MAX3 and Q1 Pro also includes a component cooling fan. |
| Gear components of hardened steel extruder | Ensure that the tool head is always fixed on a horizontal plane when moving on the x-axis. Its lightweight and high rigidity characteristics enable the tool head to move steadily and quickly along the X-axis, achieving high-speed printing. |
| Component cooling fan | Ensuring sufficient cooling of the printing layers during the printing process helps to quickly cool consumables during extrusion, allowing each layer to solidify and maintain its shape before the next layer is deposited. |
¶ Other Terms
¶ Toolhead
| Direct Drive Extruder | A direct drive extruder is a type of extruder used in 3D printing that directly mounts the filament feed mechanism on the print head, typically near the hot end. It eliminates the need for a separate filament feeding mechanism located remotely from the print head, such as a Bowden tube setup. |
| Hardened steel nozzle |
Nozzle Aperture:0.4/0.6/0.8(mm) Applicable filaments size:1.75(mm) Max Temperature:350℃ Wear-resistance, High temperature performance Thermal conductivity:220W/m.k Expansion Coefficient:8.0μm/m·℃ |
| Copper plated nozzle |
Nozzle Aperture:0.2/0.4/0.6/0.8(mm) Applicable filaments size:1.75(mm) Max Temperature:350℃ High temperature performance Thermal conductivity:330W/m.k Expansion Coefficient:16.7μm/m·℃ |
| Brass Nozzle |
Nozzle Aperture:0.2/0.4/0.6/0.8(mm) Applicable filaments size:1.75(mm) Max Temperature:350℃ Wide application with high cost performance Thermal conductivity:105W/m.k Expansion Coefficient:18.0μm/m·℃ |
| Extruder Motor | The round stepper motor which is used with the extruder. |
| Extruder | The dual gear extruder with 9.5:1 gear ratio. |
| PTFE Tube | The tube that the filament goes through from the dry box. |
| Chain Cable Carrier | The plastic section made of individual pieces that forms a chain and carry the cables and PTFE tube going to the extruder. |
¶ Heatbed
| Heatbed Signal Cable | It is a 6 pin cable that connects the MC board to the heatbed. |
| Heatbed Surface Magnet | It is a soft rubber plate with magnetic properties attached to the surface of the aluminum base plate of the heatbed. It is a component of the heatbed and its main function is to adsorb the build plate so that the build plate can be stably adsorbed on the heatbed. |
| Heatbed Unit | The main function of the heatbed is to heat the printing surface to help the printed layer adhere better to the build plate. If the printing surface is not heated, the first layer of filament deposited on the heatbed may not be able to stably adhere to the heatbed surface, causing the print to warp or even fall during subsequent printing. |
| Heatbed Sensor Unit | It is a piezoelectric ceramic with a bracket installed, and is used to detect the condition of the surface pressure on the heatbed. There are 4 sensors installed on the bottom of the heatbed. |
¶ Accessories
| Scraper | Use a sharp scraper for releasing the model from the printing surface can prolong the lifetime of the build plate. After the plate has cooled down, gently slide the scraper underneath one of the corners of the model then carefully bend the sheet to remove the model. |
| Glue Stick for Build Plate |
The glue stick creates a thin layer of adhesive on the build plate, providing a better grip for the printed object.
To use a glue stick, you typically apply a thin layer of glue evenly across the build plate.
After the print is completed and the build plate has cooled down, the printed object can usually be easily removed from the build plate. |
| Lubricant Grease and Lubricant Oil |
Lubricant Grease is used for lubricating lead screws or eliminating noise issues between belts and idler pulleys. Lubricant Oil is typically used for the lubrication of linear guides, slide rails, and steel shafts. |
| Thermal Paste | It is used to improve the thermal conductivity of hotend and nozzles. |
| Fuse | A fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. |
| U disk | Used for mobile storage media. |
| Ethernet cable | Used to connect the printer to the network. |
| 7mm wrench | Used for disassembling and replacing nozzles. |
| allen driver | Accessories are available with 1.5mm, 2.0mm, and 2.5mm hexagonal screwdrivers. |
| Clean the plug with a needle | 0.4mm through-hole needle, used as a tool to clean nozzle blockages and ensure smooth printing process. |
¶ Mechanical Structure
| CoreXY | CoreXY is a motion control system. It is named after its configuration, which consists of two stationary motors and a belt arrangement that enables precise movement in the X and Y axes. |
| Enclosed Chamber | An enclosed chamber in the context of 3D printing refers to a structure or housing that surrounds the 3D printer, providing a controlled environment for the printing process. It is designed to create a stable and enclosed space where temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors can be regulated. |
| X-axis |
High-grade hardness steel hollow linear shafts. Full-Carbon Rail (X-Smart3) |
| Y-axis | High-grade hardness steel linear shafts. |
| Z-axis | Dual screws and four linear shafts. |
| Bottom | All-metal and reinforced with metal crossbeams at the bottom. |
¶ Fans
| Hot end cooling fan | The small fan which is attached to the hotend, which helps to reduce heat transmission between the extruder and the hot end. |
| Model cooling fan | The fan is specifically designed to cool the printed layers as they are being deposited onto the print bed. |
| Motherboard fan | A fan which blows cool air over the motherboard, to keep it cool. |
| Chamber heater fan | The fan push the heating air to keep the chamber temperature. (Max chamber temperature 65℃) |
¶ Build Plate
| Hot bed | Temperature: ≤120℃, PID control |
| QIDI HF Plate | Double-Sided Flexible Magnetic HF Plate, Better surface adhesion than PEI plate. |
| QIDI smooth Plate | Double-sided PEI sheet, one side of which covered PEA film, very good adhesion, keeps the bottom of the print smooth, not as durable as HF plate. |
| Base | Steel plate + aluminium plate |
¶ Filaments
| QIDI PLA Rapido | A basic PLA filament, for beginners and complex model. |
| QIDI PLA Matte Rapido | A PLA filament with a more matte surface, for beginners and complex model. |
| QIDI ABS Rapido | ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a commonly used thermoplastic polymer in 3D printing. It is known for its strength, durability, and wide range of applications. Heated chambers print better. |
| QIDI PETG-Tough | The PETG-Tough is a rigid, tough, high-performance meterial with odorless, high impact resistance and high heat resistance. |
| QIDI ABS-GF25 | Use a special multi-layer co-extrusion technology to design the consumables into an inner and outer double-layer structure. The inner layer is ABS resin filled with 25% high content glass fiber, and the outer layer is bonded ABS resin. The duouble-layer structure is retained when the consumables are extruder from the nozzle. |
| QIDI PET-CF | PET-CF (Polyethylene Terephthalate with Carbon Fiber) is a composite filament used in 3D printing. It is a combination of PET, a popular thermoplastic polymer, and carbon fibers, which are added to enhance the material's mechanical properties. |
| QIDI PAHT-CF | PAHT-CF (Polyamide with High-Temperature Carbon Fiber) is a composite filament used in 3D printing. It combines polyamide, commonly known as nylon, with high-temperature carbon fibers to create a material with excellent strength, heat resistance, and dimensional stability. |
| QIDI PA12-CF | PA12-CF (Polyamide 12 with Carbon Fiber) is a composite filament used in 3D printing. It combines polyamide 12, also known as nylon 12, with carbon fibers to create a material with enhanced mechanical properties, strength, and dimensional stability. |
| QIDI S-White | QIDI S-WHITE can provide a moderate bond strength to the main material such as PA12-CF, ensures that the main material can be molded to the support surface and can be easily separated from the support surface when the printing is done. |
¶ Print Quality
| String | Fine filaments that appear between printed parts during 3D model printing, usually caused by leakage during traveling. |
| Ringing | It is a visual artifact that typically occurs around the sharp corners or edges of a 3D printed object, appearing wavy or rippled. |
| Clogging | It refers to the situation where the nozzle or the extruder of the 3D printer becomes clogged by filament, preventing proper extrusion or feeding. |
| Warping | When the corners of the printed object detach from the printing platform during the printing process, it can cause deformation or warping of its bottom. |
| Oozing | Oozing refers to the phenomenon that the printer nozzle accidentally leaks out the melted filament before printing the model. |
| Shrinkage | It refers to the reduction in size or volume of a 3D printed object as it cools down. |
| Spaghetti | This refers to when the printing fails, the filament extruded from the nozzle appears on the build plate like a ball of spaghetti, usually caused by poor bonding of the printed object. |
| Wear | It refers to the gradual degradation or damage of printer components or parts due to friction, abrasion, or stress. |
| Layer lines | It refer to the visible lines or ridges on the surface of a printed object caused by the layer-by-layer manufacturing process in 3D printing. |
| Under-extrusion | It occurs when the printer extruder fails to extrude enough material, resulting in gaps or missing layers on the surface of the printed object. |
| Over-extrusion | It happens when the printer's extruder pushes out too much filament, leading to excess material and poor print quality. |
| Pillowing | It occurs when the top layers of a printed object are not tight enough, resulting in visible gaps or indentations on the surface. |
| Z-banding Z | It refers to visible horizontal lines or stripes on the surface of a printed object caused by inconsistent layer height or mechanical issues with the printer's Z-axis. |
| Seam | It refers to the starting and ending points of the extruder as it prints each layer of the object. |
| Elephant Foot | In FDM 3D printing, the material is extruded layer by layer through the nozzle to construct the 3D model. So during the printing, the first layer of extruded filaments is pressed onto the heat bed and has not yet fully cooled. In addition, the compression from the upper layer of gravity may cause the printed first layer to expand, which is called elephant foot. |
| Annealing | It refers to the process of heat treatment applied to a 3D printed model, aimed at reducing internal stresses, improving material mechanical properties, and enhancing thermal stability. Annealing can be achieved by heating the model to a specific temperature and maintaining it for a period of time before allowing it to cool slowly. |