¶ Arc fitting
Most of the 3D models are composed of triangular meshes, which means that the arcs in the 3D models have been converted into curves in the STL file using a lot of short straight lines. You can check "Show Wireframe" in the "Simplify Model" function to see the triangular meshes that make up the model and the small lines that make up the arcs.
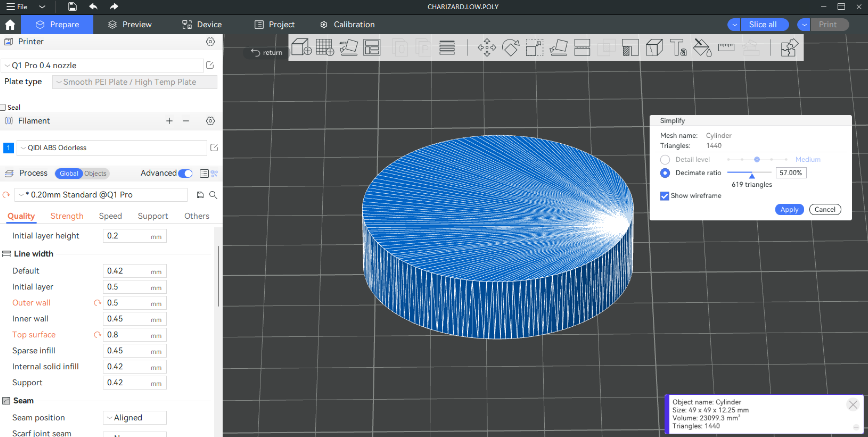
In this way, in the final slicing and printing, the tool head will also move and print according to this path. When the printer speed is slow, these dense paths have no obvious bad effect on print quality. However, when the printing speed is high, a large number of transient pulse signals will be generated at the turning point of the line segment, which will bring noise and vibration.
To remedy this problem, QIDI studio generates arc move paths by fitting them within certain acceptable tolerances, so that the resulting Gcode supports G2/G3 arc move. This can reduce the number of turning point of segments and make path more smooth, and reduce the vibration in the fast printing.
The arc fitting method is based on ArcWelderLib. Sincere thanks for opening the source code for such excellent work.
¶ Operation
Here you can enable/disable the arc fitting function.
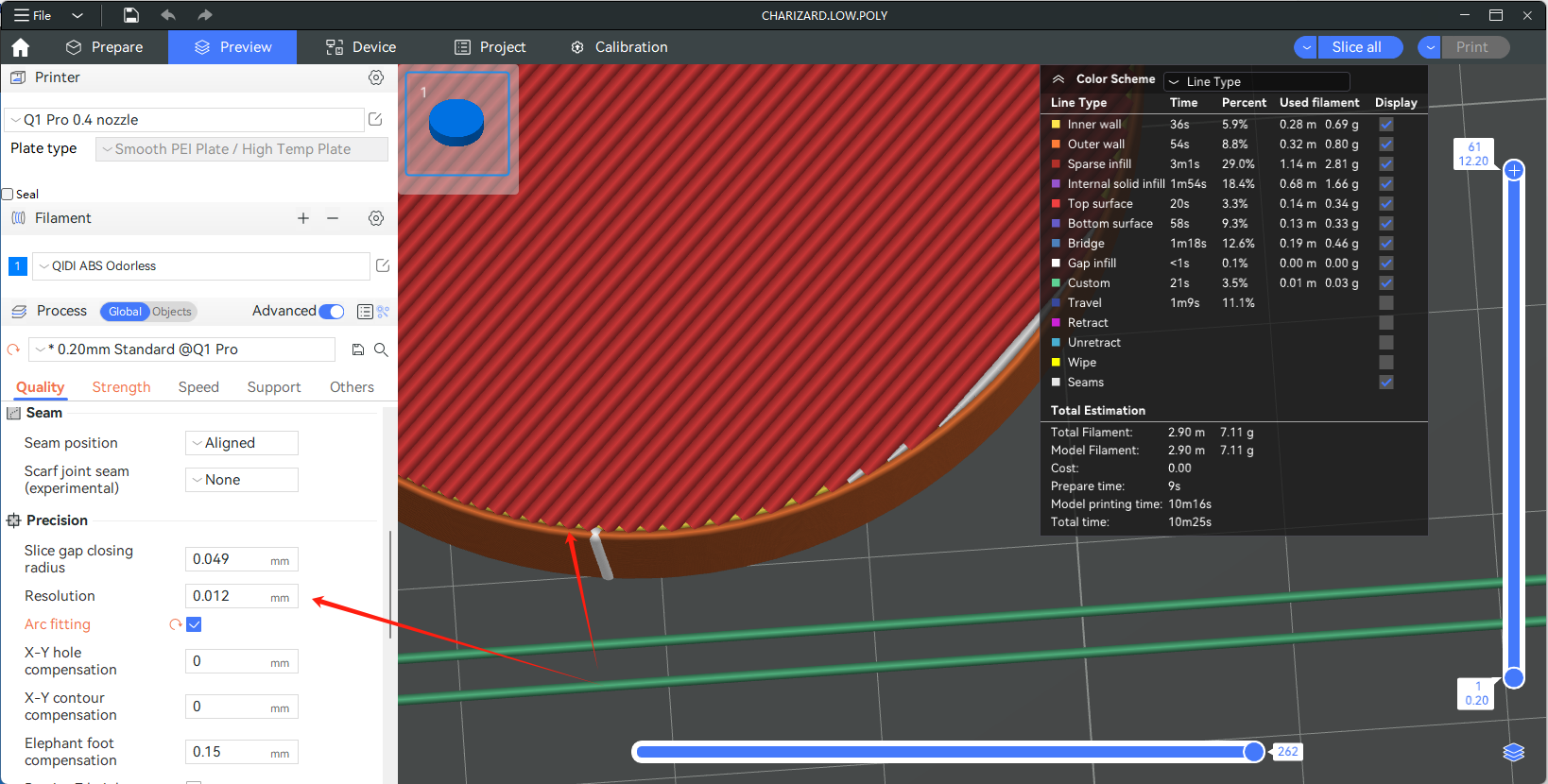
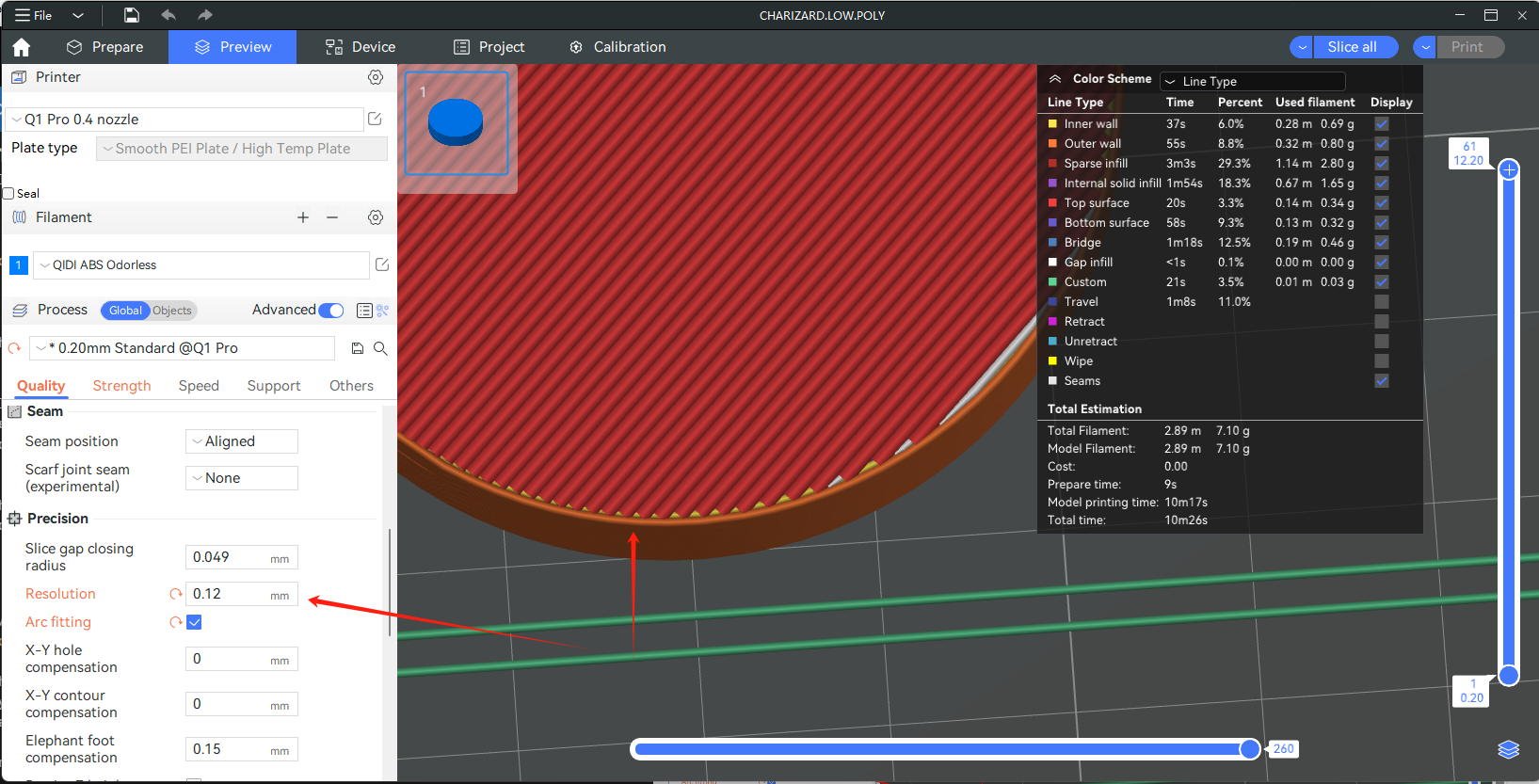
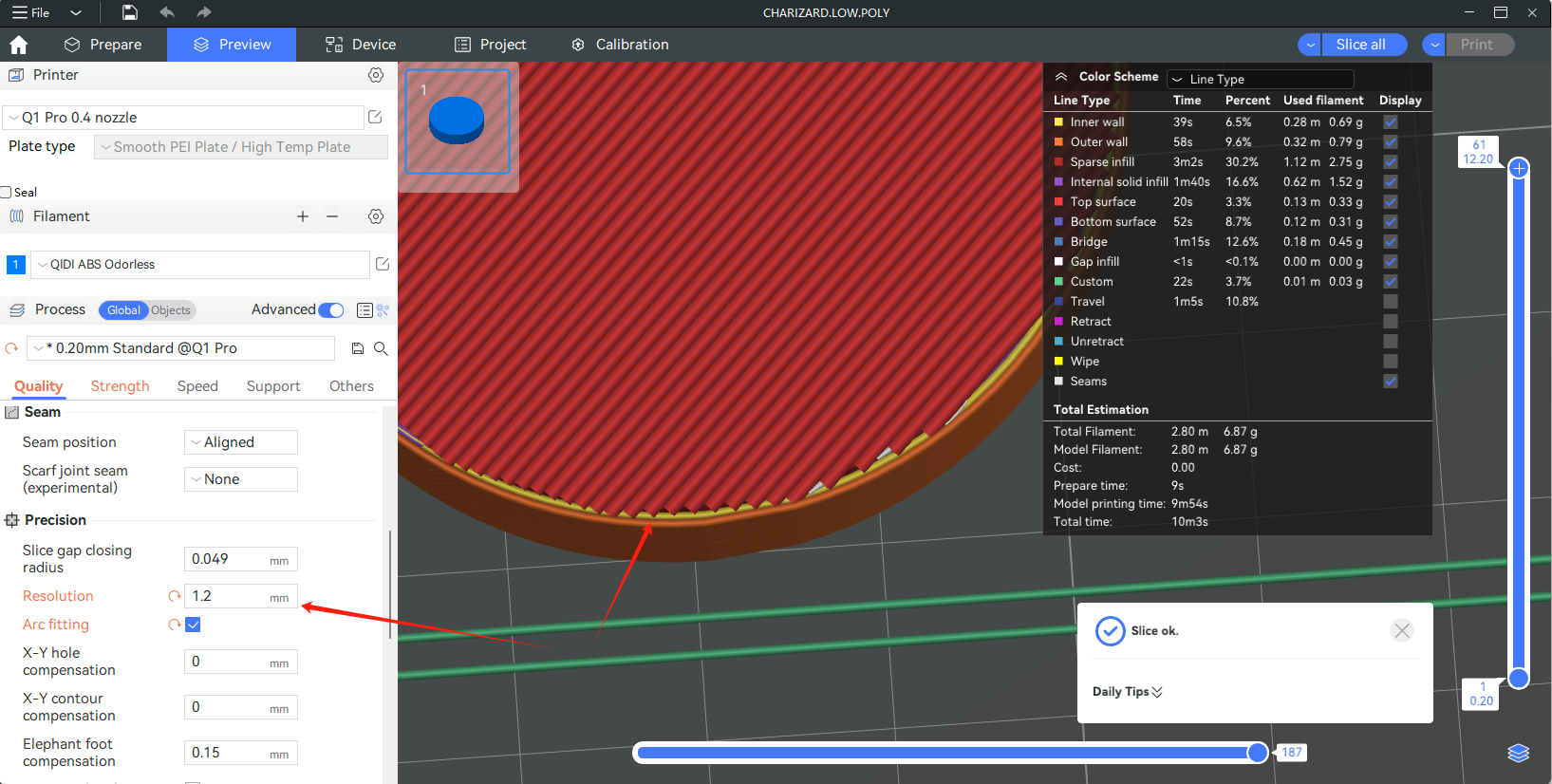
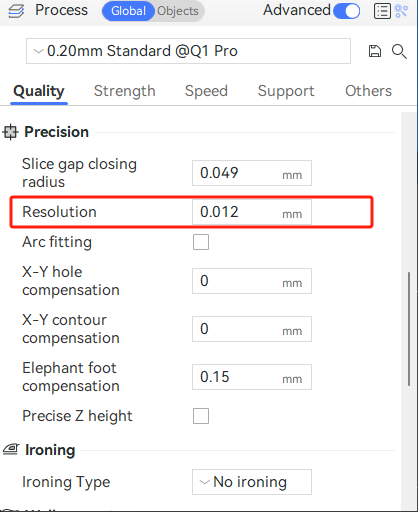
The resolution is the maximum deviation of the fitted path of the arcs from the original path (bow height error), and you can decrease the resolution (increase this value) to add more arcs after slicing to an less accurate model. We usually don't recommend setting this value too large, though. If you try to force a model with low accuracy into arcs by setting a larger resolution, the model will show significant misalignments between layers, or even cause the model to be completely distorted.
Comparison of curved surfaces at different resolutions: